Meeting of health center staff in Guinea in support of health service delivery improvements. Photo credit: URC
Health Evaluation and Applied Research Development (HEARD)
The Challenge
Implementation of lifesaving health care practices, policies, and strategies benefit from evidence and data that can inform real-time improvement. There is often a disconnect between evidence producers, such as research and academic institutions, and the community of evidence users, such as policymakers and program implementers. Alignment of priorities and more strategic engagement of these actors can facilitate the use of more relevant and responsive evidence for decision-making to improve implementation of health programs.
Overview and Objectives
The Health Evaluation and Applied Research Development (HEARD) Project is a flexible global implementation science (IS) partnership mechanism that responds to emerging USAID health and development priorities.
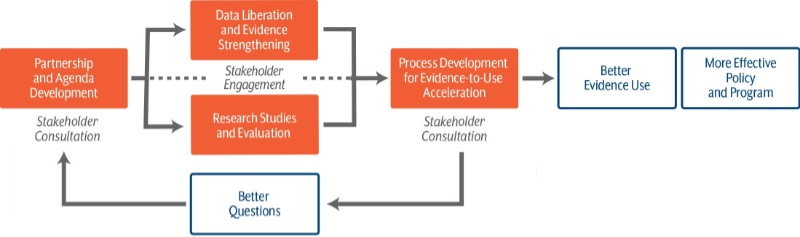
The project leverages learning collaborations, where a diverse range of stakeholders share learning related to a specific health area and jointly generate evidence and accelerate the use of that evidence to improve policy and program implementation globally.
HEARD lays the foundation for a global Implementation Science Collaborative (ISC) – a network of learning networks – covering a range of priority areas in health.
HEARD’s topic-specific learning collaborations focus on urban health, respectful maternal care, post-partum hemorrhage, social accountability, violence against children/child safeguarding, mental health and psychosocial support, and assistive technologies for those with mobility impairments.
The project’s core strategies involve:
- Developing priorities that are relevant across different groups of health stakeholders through their engagement in learning collaborations and consultations;
- Data liberation and evidence strengthening to better leverage existing evidence and data;
- Evidence generation through new research studies and evaluation; and
- Evidence-to-use acceleration through continuous strategic communication, knowledge sharing, and stakeholder engagement.
Implementation science activities are facilitated by HEARD’s expansive partnership, comprised of more than 35 institutions with a range of functions, expertise, and geographic and strategic positioning. As the project lead, URC serves as the Research Systems Integrator, fostering alignment of purpose, partners, and process within thematic area collaborations. Proper alignment results in improved questions, higher demand for evidence among decision-makers, and accelerated uptake of evidence to inform policy and programming.
Achievements
HEARD has proven to be a flexible mechanism that leverages a partnership to address a wide range of health issues. HEARD’s global efforts currently span 19 countries. The project has established more than six active learning collaborations. Learning collaboration activities include more than 20 ongoing or completed research studies, two global evaluations, and four country-specific evaluation activities, with a number of emerging research activities planned. Illustrative highlights of HEARD’s results include:
- Country-based evaluations have informed future U.S. Government bilateral investments;
- Evidence generated on reproductive, maternal, child, and urban health have informed East, Central, and Southern Africa Health Community’s Ministerial Resolutions on urban health, respectful maternity care, and protecting children from violence; and
- The Advancing Post-Partum Hemorrhage Care Partnership developed by HEARD in Malawi and Madagascar tested and implemented innovative mentorship models for health providers.
HEARD Project Evaluations
- Midterm Evaluation of USAID Jordan Health Service Delivery Activity
- Final Evaluation of USAID Guinea’s Health Service Delivery Activity
- Assessment of Positive Youth Development
- Midterm Evaluation of USAID’s Global Health Program Cycle Improvement Project
- GHIS Burkina Faso: Improving Malaria Care (IMC) Project Evaluation
- Scoping an Evaluation of USAID Nigeria’s Integrated and Vertical Malaria Programs